Manufacturing Sector
Quick Introduction:
The manufacturing sector stands at the confluence of physical production and digital innovation, making it uniquely vulnerable to a spectrum of cyber-security threats. From the shop floor to the executive office, integrating cyber-security into the manufacturing process is no longer optional but a necessity. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), ransomware, phishing, and insider threats, alongside the increasing reliance on the Internet of Things (IoT), present complex challenges that can disrupt operations, compromise intellectual property, and undermine the trust of partners and customers.

Cyber-security Regulations
In the UK, the manufacturing sector must navigate a robust landscape of cyber-security regulations to protect its digital and physical assets. Compliance is not just about legal adherence but ensuring resilience against cyber threats.
UK-GDPR: Prioritizing Data Privacy In Manufacturing
Adapting the principles of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the UK-GDPR is pivotal in protecting personal data. Manufacturers with operations in the UK must adhere to its principles, ensuring data protection by design and by default, and be prepared for stringent enforcement and hefty fines for non-compliance.

Compliance Steps:
- Understand the data protection principles set out by the UK-GDPR.
- Implement adequate measures to secure personal data, such as encryption and access control.
- Ensure that there are procedures in place to handle data subject rights requests.
- Maintain detailed records of data processing activities.
- Appoint a dedicated Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance.
- Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk processing.
- Foster a culture of data protection awareness across the organization.
PCI-DSS: Securing Cardholder Data
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) applies to manufacturers that process, store, or transmit credit card information. Compliance ensures the security of card transactions and protects against cardholder data breaches.

NIST Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides manufacturers with a structure to manage and mitigate cyber-security risk, particularly useful for those engaged in high-value manufacturing or with significant intellectual property concerns.
- NIST guidelines for supply chain risk management
- Manufacturers are advised to include cyber-security criteria in the supplier selection process and to continuously monitor suppliers' compliance with cyber-security requirements.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement
- NIST advocates for an adaptive approach to cyber-security, emphasizing the need for ongoing assessment and real-time improvements to security measures.
Data Protection Act 2018
Supplementing UK-GDPR, the Data Protection Act 2018 governs the processing of personal data. Manufacturers must be cognizant of their obligations under this act, including data subject rights and the conditions for lawful processing.
- Implications for manufacturing data handlers
- The Act imposes clear protocols for responding to data breaches and stresses the importance of appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) where necessary.
- Security governance and accountability
- Manufacturers must not only protect data but also demonstrate their data protection activities, highlighting the governance and accountability within their practices.

Cyber Essentials:
Cyber Essentials is a government-backed scheme that gives organizations a clear baseline for cyber-security. Manufacturers can achieve certification to demonstrate to partners, suppliers, and customers that they have essential protections in place.
It's particularly relevant to manufacturers as it addresses fundamental technical controls across five key controls:
Boundary firewalls and internet gateways
Secure configuration
Access control
Malware protection
Patch management
Certification under this scheme not only helps in safeguarding against common cyber threats but also demonstrates to customers that the manufacturer takes cyber-security seriously, enhancing trust and reputation.

IoT Testing:
With IoT devices becoming integral to manufacturing operations, IoT security testing ensures that devices are not vulnerable to attacks. This includes regular vulnerability scanning and testing to mitigate risks from connected devices.
- Regular security assessments for IoT devices
- Manufacturers should conduct security assessments of their IoT devices to uncover and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Mitigation strategies for common IoT vulnerabilities
- Implementing strong authentication, ensuring data encryption, and segmenting IoT devices from critical networks are essential strategies to mitigate risks associated with IoT devices in the manufacturing environment.

ProCheckUp Solution's
For UK-GDPR Compliance:
- IASME Cyber Essentials: A certification that verifies basic cyber-security hygiene, ensuring that Manufacturing organisations have fundamental security controls in place to protect against common cyber threats. (Learn More)
- IASME Cyber Assurance: This includes a GDPR readiness assessment to ensure that all aspects of data privacy and security are addressed, thus aligning with the GDPR’s stringent requirements.(Learn More)

For Data Protection Act 2018 Adherence:
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA): Services to help manufacturing organisations conduct assessments that evaluate the impact of new projects or technologies on the privacy and security of personal data.(Learn More)
- Data Governance Consulting: Expert consultancy to ensure the correct handling of personal data across all operations, aligning with the Data Protection Act’s provisions.

For PCI-DSS Compliance:
- PCI-ASV (Approved Scanning Vendor) Services: ProCheckup, a globally recognized ASV, conducts meticulous external vulnerability scans to ensure the integrity of systems handling credit card data, in compliance with PCI-DSS requirement 11.3.2. Our ASV scan solution leverages cutting-edge security tools to rigorously test and confirm your network's defenses against known threats, helping to secure your data transactions. (Learn More)
- PCI-QSA (Qualified Security Assessor) Services: As an independent QSA firm accredited by the PCI Security Standards Council, ProCheckup embodies excellence in ensuring entities meet the stringent standards of PCI DSS. Our longstanding expertise, since the establishment of the QSA program, provides reliable validation of your compliance posture. (Learn More)
- Penetration Testing: ProCheckup's penetration testing services are an embodiment of our commitment to security excellence, meeting PCI-DSS requirement 11.4.1. Our team of Crest, Cyberscheme, and NCSC-qualified penetration testers, with a proven 24-year track record since 1999, employs a comprehensive approach to identify and remediate exploitable security vulnerabilities. (Learn More)
- Data Discovery for Primary Account Number (PAN): Our specialized services extend to the detection of PAN within your network, particularly identifying unauthorized storage locations outside the Cardholder Data Environment (CDE), adhering to PCI-DSS requirement 12.5.2. ProCheckup ensures that sensitive payment data is contained and managed securely. (Learn More)
- Segmentation Testing: With precise technical testing, ProCheckUp validates the efficacy of network segmentation, ensuring that the CDE is isolated from all systems not pertinent to card processing , in compliance with PCI-DSS requirement 11.4.5 This critical service supports PCI-DSS compliance by verifying the robustness of segmentation controls, maintaining the security of your cardholder data environment. (Learn More)
- Wireless Testing: Adhering to the stringent standards of PCI-DSS requirement 11.2.1, our team conducts comprehensive wireless testing quarterly. This process is meticulously designed to uncover and assess both sanctioned and unsanctioned wireless access points within your network, ensuring a robust security posture. (Learn More)

For Mitigating Supply Chain Vulnerabilities:
- In the current digital landscape, the inter-connectivity with suppliers and partners significantly widens the scope of potential threats. Our comprehensive Supply Chain Testing service is designed to empower businesses to identify, comprehend, and mitigate the myriad risks that stem from third-party collaborations. (Learn More)
For Combating Phishing and Social Engineering:
- The human element often presents the most significant security risk. Phishing and social engineering attacks are deceptively designed to exploit this vulnerability by manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information or providing unauthorized access. Our proactive approach begins with in-depth Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) gathering to construct a credible pretext. We then conduct simulated phishing expeditions using realistic scenarios that mirror actual threats, thereby training your workforce to recognize and counteract such deceptive tactics effectively.(Learn More)
For Securing the Internet of Things (IoT):
- The manufacturing sector's growing reliance on IoT devices for inventory management and enhanced customer experiences brings with it an urgent need for robust security measures. Our IoT Security Reviews are at the cutting edge, aligning with the rapid pace of digital transformation.(Learn More)
Maintaining compliance with these regulations is crucial for the manufacturing sector not just for legal integrity but also for maintaining customer trust. The assurance that a manufacturer is following stringent cyber-security practices can be a significant competitive advantage. Compliance ensures operational resilience, reduces the risk of financial penalties, and enhances customer confidence in the manufacturer.
For businesses in the manufacturing sector, this means implementing robust cyber-security policies, continuously educating staff about security best practices, and regularly reviewing and updating security measures to address new and emerging threats.
Practical Implementation Strategies for Cyber-security in Manufacturing:
After understanding the regulatory landscape, manufacturing businesses must translate these requirements into actionable strategies. Here are key steps for retailers to take in implementing robust cyber-security measures:
Visual Representation of Compliance
Manufacturers should aim to visualize their compliance journey, allowing for transparent communication with stakeholders about their cyber-security posture. This can be done through:
- Infographics: Showing compliance roadmaps, certification processes, and security control implementations.
- Dashboards: Real-time monitoring of network health, threat detection, and security incident responses.
- Educational Content: Simplified explanations of regulations and requirements for employees and clients through engaging multimedia.
Cybersecurity Culture in Manufacturing
Building a strong cyber-security culture within the manufacturing sector involves:
- Training and Awareness: Regularly scheduled training sessions for employees to recognize threats and understand protocols.
- Incident Response Drills: Simulated cyber-attacks to prepare the workforce for real incidents, ensuring a swift and effective response.
- Employee Engagement: Encouraging employees to take an active role in cyber-security, reporting anomalies and suggesting improvements.
Future-Proofing with Cyber-security
As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, staying ahead in cyber-security means:
- Innovative Defense Strategies: Adopting AI and machine learning for predictive threat detection and adaptive security measures.
- Investment in R&D: Committing resources to explore new cyber-security technologies and practices that can better protect manufacturing environments.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with cyber-security firms and participating in industry-wide security initiatives to benefit from shared knowledge and resources.
Creating a Cyber-Resilient Manufacturing Ecosystem
A comprehensive cyber-security strategy in manufacturing should focus on resilience, ensuring that operations can withstand and recover from cyber incidents:
- Redundancy and Fail-safes: Implementing backup systems and processes that can take over in case of a cyber incident to minimize downtime.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting internal and external cybersecurity assessments to validate and improve security measures.
- Supply Chain Security: Extending cyber-security practices to the supply chain, requiring partners and vendors to meet specified security standards.
Cybersecurity and Industry 4.0
With Industry 4.0 revolutionizing manufacturing, cyber-security becomes even more pivotal. Embracing the fourth industrial revolution requires:
- Smart Factory Security: Safeguarding connected manufacturing systems and smart machinery from emerging threats.
- Data Analytics for Security: Utilizing big data analytics to detect subtle anomalies that could indicate a security breach.
- Interoperability and Security: Ensuring that as systems become more interconnected, they also remain secure against cyber threats.
Vendor and Third-Party Management:
- Establish strict security criteria for vendors and third-party service providers.
- Regularly assess third-party risks and ensure external partners adhere to the same security standards required of the retail business itself.
Customer Data Rights and Transparency:
- Clearly communicate to customers how their data is being used, stored, and protected.
- Develop simple and efficient procedures for customers to exercise their rights under the UK-GDPR, such as accessing their data or requesting deletion.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In closing, the cyber-security landscape for the UK manufacturing sector is complex but navigable with the right knowledge and tools. Manufacturers are encouraged to:
- Assess their Current Posture: Taking stock of current cyber-security measures and identifying gaps.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Consulting with cyber-security experts to develop and implement a comprehensive strategy.
- Stay Informed and Compliant: Keeping up-to-date with the latest regulations and cyber-security best practices.
Manufacturers who prioritize cyber-security will not only protect their operations and reputation but also gain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital and connected industry.

Cybersecurity Process Flow Chart
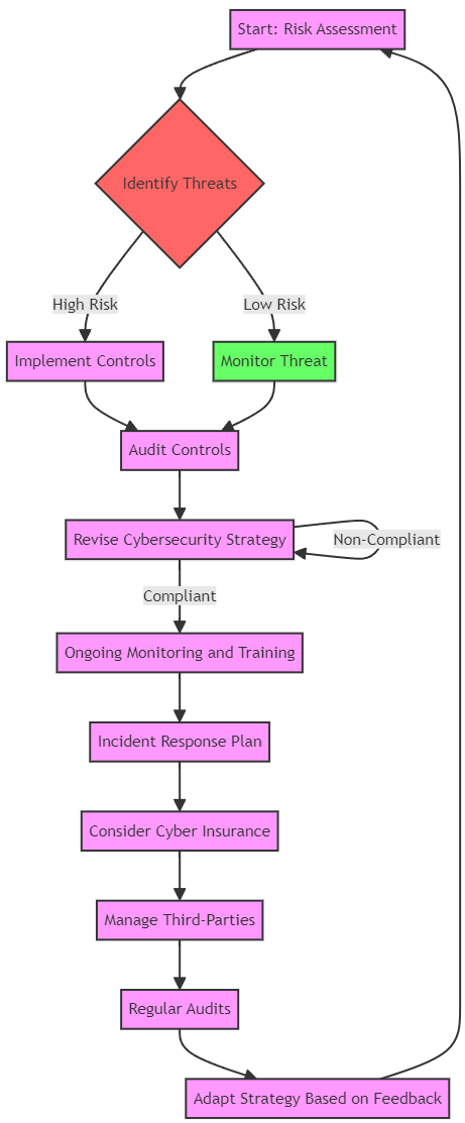
Cybersecurity Collaboration and Sharing
In addition to the internal measures, it is crucial for manufacturing organisations to actively participate in sector-wide cyber-security initiatives. These include:
- Information Sharing: Engaging in information sharing platforms to receive timely alerts on threats and share best practices with industry peers.
- Regulatory Engagement: Maintaining an open dialogue with regulators to stay ahead of new regulations and to influence policy development with real-world insights.
- Global Cybersecurity Standards: Aligning with global cyber-security standards and frameworks, such as ISO/IEC 27001, to ensure a consistent approach to managing information security.
- Cybersecurity Advocacy: Advocating for stronger cyber-security measures and more substantial investments in cyber-security at industry conferences and in public forums.

With these resources and strategies in place, manufacturing organisations can better anticipate and counteract the evolving cyber threats they face, ensuring trust and continuity in the digital age.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






