Incident Response And Forensics:
Proactive Measures In A Reactive World
Every organization, no matter its size or sector, is susceptible to cyber threats. When incidents occur, the speed and efficiency of your response can make all the difference. Welcome to our comprehensive guide on incident response.
What is Incident Response?
Incident Response (IR) refers to the process followed by an organization to handle a cyber security event or incident. The objective is not just to handle the situation, but to manage it in a way that limits damage, reduces recovery time and costs, and mitigates the impact on the business.

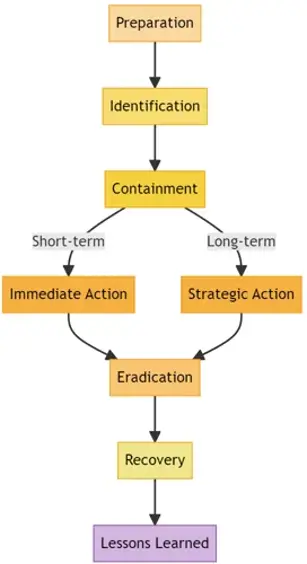
The Incident Response Lifecycle:
- Preparation: This step involves establishing and maintaining an incident response plan, developing IR policies, and setting up communication strategies for incidents.
- Identification: It’s about detecting and acknowledging the incident. This involves monitoring security events to identify abnormal patterns.
- Containment: Once an incident is identified, it's crucial to contain the threat. Containment is usually split into short-term (immediate action) and long-term (strategic action) solutions.
- Eradication: After containment, find the root cause of the incident and remove the threat source.
- Recovery: Restore and validate system functionality for business operations to resume. Monitor for signs of threats that might have been activated by the original incident.
- Lessons Learned: After handling the incident, conduct a retrospective of the incident. What went well? What could have been done better? What can be improved for future responses?
Building an Incident Response Team (IRT):
Selecting the right personnel for your incident response team is a crucial step. This team should ideally consist of:
- Incident Response Manager: This individual oversees the entire response process, making crucial decisions, and ensuring communication flows seamlessly between all involved parties.
- Security Analysts: They are responsible for identifying the nature of the breach, its source, and potential remedies.
- Network Engineers: Their expertise helps in tracking the intrusion method, sealing breaches, and restoring secure network functionality.
- Forensic Experts: Post-incident, these professionals determine how the breach occurred, the extent of the data compromised, and recommendations for preventing similar incidents.
- Legal and Compliance Professionals: They provide guidance on regulatory obligations and help manage any potential legal fallout from the breach.
- Public Relations and Communications Specialists: In the event of a breach becoming public knowledge, this team manages the company's image and communication to stakeholders.
Incident Response Tools and Technologies:
Equipping your IRT with the right tools is vital. Some essential tools include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collects and analyzes logs and data from various systems to provide real-time analysis of security alerts.
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Provides visibility into endpoint actions and allows for quick response to threats.
- Forensic Tools: Help in gathering evidence after a security incident to understand its nature and origin.
The Importance of a Well-Defined Incident Response Plan
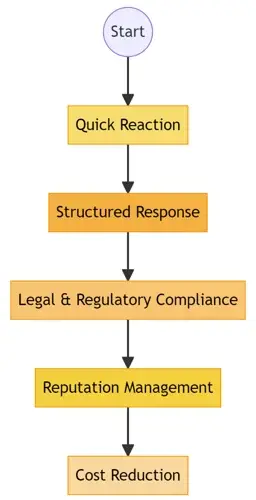
In the fast-paced world of cyber threats, an effective incident response plan (IRP) can be the shield that protects an organization from significant losses. A clear IRP offers:
Quick Reaction: Minimize the window of exposure to threats, thereby reducing potential damage.
Structured Response: A systematic approach ensures no crucial steps are overlooked.
Legal & Regulatory Compliance: Certain industries require a set IR procedure to comply with standards and regulations.
Reputation Management: Swiftly addressing and resolving incidents can mitigate negative public perceptions.
Cost Reduction: Efficient responses can decrease the financial impact of security incidents.
Tabletop Exercises: Practice Makes Perfect
Tabletop exercises are simulated cyber incidents that test an organization's response capabilities. These exercises:
Validate the IR Plan: Ensure that the response plan is not just theoretical but also practical.
Train the IRT: Members of the Incident Response Team can sharpen their skills in a controlled environment.
Identify Gaps: Discover weak spots in your response strategy that might go unnoticed without testing.

Communication During an Incident
Clear and timely communication is paramount during a security breach:
- Internal Communication: Ensure that all relevant personnel, from top-level executives to the tech team, are aware of the situation.
- External Communication: If required, notify affected customers, partners, and stakeholders about the incident, potential impacts, and the steps you are taking.
- Media Handling: Have a trained spokesperson to address media inquiries, ensuring consistent and accurate information is disseminated.
- Legal Considerations: Always have a legal counsel review communications, especially if the incident involves data breaches or regulatory implications.
- Aftermath: Post-Incident Analysis and Reporting
Best Practices for Incident Response
Adopting a proactive stance in managing incidents can drastically reduce potential damages and recovery time. Here are some best practices to incorporate into your incident response strategy:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement monitoring tools that provide real-time analytics of your network traffic to detect anomalies.
- Frequent Backups: Regularly back up all critical data, ensuring that backups are stored in secure locations, both on-site and off-site.
- User Awareness Training: Many breaches result from human error. Educate employees on security protocols and the importance of vigilance.
- Incident Response Drills: Simulate cyberattacks to test your team's preparedness. This will identify gaps in your response strategy.
- Engage Legal Counsel: Understand the legal implications of a breach, especially concerning data privacy laws and regulations.
- Collaboration with Other Organizations: Share intelligence and strategies with peer organizations. A threat to one is often a threat to many.
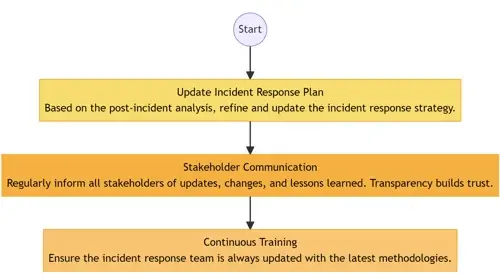
Lessons Learned: Convene the response team and stakeholders to discuss what went right, what went wrong, and areas of improvement.
- Update Incident Response Plan: Based on the post-incident analysis, refine and update the incident response strategy.
- Stakeholder Communication: Regularly inform all stakeholders of updates, changes, and lessons learned. Transparency builds trust.
- Continuous Training: Ensure the incident response team and employees, in general, are trained periodically based on the latest threat intelligence.
Incident Classification & Prioritization
Not all cyber incidents are of the same magnitude. Classification and prioritization are crucial:
- Severity Level 1 (Critical): These are large-scale incidents, potentially affecting critical assets or a significant number of users. Requires immediate attention.
- Severity Level 2 (High): Not as widespread as critical incidents but can cause significant harm if not addressed promptly.
- Severity Level 3 (Moderate): Has limited scope and impact but still warrants attention.
- Severity Level 4 (Low): These are minor incidents with minimal impact and can often be addressed in routine processes.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The cyber landscape is ever-evolving, and so should be your incident response strategy:
- Regularly Update the IRP: As new threats emerge and organizational infrastructure changes, update your IRP accordingly.
- Frequent Training: Organize periodic training sessions for the IRT to acquaint them with new tools and response strategies.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage all stakeholders to provide feedback post-incident. This can help in refining the response process.
Incident Response Retainers
Many organizations opt for incident response retainers with cybersecurity firms. These arrangements provide:
- Immediate Access to Experts: In case of an incident, having a retainer means priority access to specialized skills.
- Proactive Services: Some retainers offer periodic security assessments, ensuring your defenses are robust.
- Cost Predictability: Retainers can be budgeted, unlike unforeseen costs from unexpected breaches.
- Incident Reporting and Stakeholder Communication
Final Thoughts
Every organization must recognize that in the current digital climate, preparedness for cyber incidents is not a luxury but a necessity. Building a comprehensive incident response strategy, coupled with regular training and the right tools, lays the foundation for resilience in the face of inevitable cyber threats.
Contact us to enquire about our range of services including:
Breach Impact Assessments
As part of an incident investigation ProCheckUp can perform a breach impact assessment identifying: Read more...
eDisclosure\eDiscovery
The ProCheckUp Forensic Services team of highly skilled professionals leverage the know-how and support of our team of specialists in digital data to help our clients address the complexities associated with eDisclosure (eDiscovery in the United States or eDisclosure in the United Kingdom) and information governance through the delivery of a comprehensive set of services and solutions. Read more...
Forensics
Our consultants have a vast experience in the area of computer and mobile forensics, data recovery and data discovery. Read more...
Forensics Readiness Plan
ProCheckUp can help organisations prepare themselves better in anticipation of an attack by providing assistance and guidance in the following areas:Read more...
Gold Teaming
Gold teaming identifies improvements in your internal and external communications, crisis management procedures and decision making...Read more...
Malware Reverse Engineering
If an organization discovers or suspects that some malware may have gotten into its systems, ProCheckUp's response team may wish to perform malware analysis on any potential samples that are discovered during the investigation process to determine if they are malware andRead more...
Instrusion analysis - Compromise Assessment
If you have recently been a victim of a cyber-attack, ProCheckUp will be able to provide assistance in identifying and analysing the attack to gauge the severity and determine whether the incident has been successful in compromising the confidentiality, integrity or availability of your information system.Read more...
Incident Response
Organisations rarely have an adequate incident response plan in place to prepare for any unprecedented system and network compromise. ProCheckUp can provide proactive and reactive incident response services to support an organisation before, during and after a computer security incident as well as helping determine the best implementation for system monitoring across the network. Read more...
Technical Services Counter Measures (TSCM)
Is the process of bug-sweeping or electronic countersurveillance. It is related to ELINT, SIGINT and electronic countermeasures (ECM). ! Read more...
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






