Securing Your eCommerce Platform
A Guide to Enhanced eCommerce Security

In the modern age, where online shopping has become a staple of our daily lives, the security of eCommerce platforms has become a necessity. With each passing year, the evolution of cyber threats unveils new risks, challenging the resilience of online businesses and the safety of their customers. . From sophisticated data breaches and innovative types of cyber-attacks to fraudulent transactions, the robustness of eCommerce platforms is constantly tested. However, the complexity of cyber-security is often viewed as daunting. That's where ProCheckUp steps in – to unravel these complexities and navigate you through fortifying your eCommerce platform effortlessly.
Why eCommerce Security Matters More Than Ever
In a world interconnected by the web, your online storefront is the face of your business. Just as you would lock up a physical store and secure your inventory, your online shop requires protection against the myriad of cyber threats lurking in the digital shadows. A breach not only affects your bottom line but can severely damage your reputation and trust with customers.
The Foundations of eCommerce Security
Building a secure eCommerce platform starts with understanding the fundamentals. This guide draws upon industry cyber-security standards, including Cyber Essentials and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), translating complex requirements into actionable steps for your business.
Firewalls and Network Security
Firewalls play a pivotal role in securing your eCommerce platform, acting as the digital equivalent of a fortress's walls. In the realm of network security, understanding how to effectively employ firewalls can significantly enhance your defences against a myriad of cyber threats. Here's a closer look at how firewalls function as your first line of defence and the steps you can take to optimize their effectiveness.

Understanding Firewalls
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organisation's previously established security policies. At its core, it's a barrier between your secure internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. A set of defined rules dictates which traffic is allowed or blocked, helping to prevent cyber attackers and malicious software from accessing your network and data.
Types of Firewalls for eCommerce Security
- Packet Filtering Firewalls: The most basic form of firewalls that make decisions based on the source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: More advanced than packet filtering, these firewalls keep track of active connections and make decisions based on the state of the connection.
- Proxy Firewalls (Application-Level Gateways): These firewalls act as an intermediary between users and the internet, providing detailed, application-level security.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW): These combine the capabilities of the above firewalls with additional features like deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention system with the ability to identify and block malicious traffic real time.
Implementing Firewalls for eCommerce Security
- Choosing the Right Type of Firewall: Depending on the size of your eCommerce environment, complexity of your network, and specific security needs, select a firewall that best suits your environment. For many small to medium-sized environment, a next-generation firewall provides comprehensive protection.
- Configure Firewall Rules: Clearly define what traffic is allowed and what should be blocked. This includes blocking traffic from known malicious IP addresses, restricting access to certain ports, and only allowing necessary protocols.
- Regular Updates and Maintenance: Like any other system, firewalls require regular updates to ensure they are protecting against the latest threats. Regularly check for firmware updates from the manufacturer and apply them promptly.
- Incorporate Into a Larger Security Strategy: While firewalls are an essential component of network security, they should not be the only tool in your arsenal. Combine them with other security measures such as intrusion detection systems, encryption, and a robust security policy to create a multi-layer defence strategy.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor firewall logs for suspicious activity. Regular reviews of firewall rules and configurations can help you adapt to emerging threats and changes in your network.
Secure Configuration
Ensuring your systems are securely configured is a critical step in protecting your eCommerce environment from potential cyber threats. An optimally configured system can significantly reduce vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit.
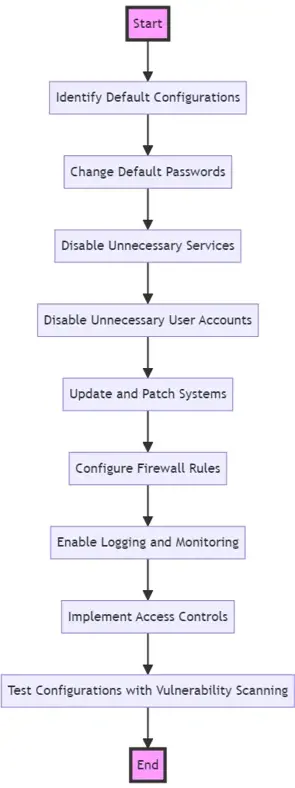
Description of Each Step:
- Identify Default Configurations: Assess your environment to identify any default settings provided by manufacturers or software providers.
- Change Default Passwords: Replace any default passwords with strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Turn off services and features not required for business operations to minimize potential entry points for attackers.
- Disable Unnecessary User Accounts: Remove or disable user accounts that are not in use to reduce the risk of unauthorised access.
- Update and Patch Systems: Regularly apply software updates and patches to fix vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Configure Firewall Rules: Set up firewall rules that only allow necessary network traffic and block known malicious traffic.
- Enable Logging and Monitoring: Activate system logging and monitoring to detect and respond to suspicious activities quickly.
- Implement Access Controls: Define and enforce policies on who can access what data and systems within your organization.
- Test Configurations with Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct vulnerability scans to identify and remediate any security weaknesses in your configurations.
- Review and Audit Regularly: Regularly review and audit your system configurations and security measures to ensure they remain effective against evolving threats.
Regular Updates and Patch Management
Regular updates and patch management are crucial components in maintaining the security of any digital platform, akin to renewing the locks on your doors as new lock-picking techniques emerge. In the realm of cyber-security, this practice ensures that vulnerabilities in software are addressed promptly, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorised access or data breaches.

Why Regular Updates and Patch Management Matter:
- Closing Security Gaps: Just as a lock might have vulnerabilities to certain lock-picking methods, software too can have vulnerabilities. Hackers actively seek these out. Regular updates patch these vulnerabilities, making it harder for cyber-criminals to exploit them.
- Enhancing Features: Updates often come with new features or improvements to existing ones, similar to a new lock offering a more user-friendly interface or stronger materials. For software, this might mean better performance or new functionalities that can improve user experience and security.
- Compliance: Many regulatory bodies require that software is kept up to date as part of compliance standards. Failing to do so can lead to penalties, much like failing to comply with building codes or security standards can have legal repercussions.
- Maintaining Compatibility: Regular updates ensure that software remains compatible with other systems and technologies. This is akin to making sure a new security system is compatible with the existing doors and infrastructure of a building.
Strategies for Effective Updates and Patch Management
- Automate Updates Where Possible: Automation tools can help ensure that software updates are applied as soon as they're available, much like automatic lock systems that rekey themselves periodically.
- Prioritise Updates Based on Risk: Just as some doors may need stronger locks due to their location or what they protect, software updates should be prioritized based on the risk and impact of potential vulnerabilities.
- Educate Users: Users should understand the importance of updates, akin to knowing why it's important to lock doors in a building. Educating users about the risks of delaying software updates can encourage prompt action.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly review your patch management policies and the status of applied updates, similar to conducting routine security audits to ensure all locks are functioning as intended.
Access Control and Authentication for eCommerce Security
Access Control and Authentication forms the cornerstone of securing your eCommerce platform. By managing who can access your platform, you ensure that only authorised users can access it. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) by adding an additional layer of security, significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access and data breaches. Let's delve deeper into these concepts to understand their importance and implementation.

Understanding Access Control
Access control is the selective restriction of access to data. It's about ensuring that the right people have the right access at the right times, with the right privileges. This process involves identifying, authenticating, and authorising individuals or groups to have access to applications, systems, or resources by associating user rights and restrictions with the established identities.
Types of Access Control:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Access is determined by the owner of the information or resource.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access decisions are made based on the regulations set by a central authority.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access is granted based on the role of the user within the organization, and rights are adjusted according to the responsibilities necessitated by that role.
Implementing Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user, machine, or entity before granting access to resources in a system. It's akin to verifying a key fits a lock before allowing entry. Authentication methods vary in complexity and security, from something as simple as a password to more sophisticated systems like biometric verification.
Strong Authentication Practices:
- Passwords: While basic, strong, unique passwords are still effective when used correctly. Encourage or enforce a policy of complex, hard-to-guess passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring two forms of identification. Typically, this involves something the user knows (a password) and something the user has (a security token or smartphone app).
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Takes 2FA a step further by adding additional verification factors, making unauthorized access significantly more challenging.
The Role of MFA in eCommerce Security
MFA is particularly crucial in the context of eCommerce platforms, where financial transactions and personal data are routinely processed. By requiring two or more verification factors, MFA ensures that the risk of fraudulent transactions and data theft is minimised. It's a security measure that offers protection even in instances where a password might be compromised.
Implementing MFA:
- Choose the Right MFA Solution: Consider the needs of your users and the level of security required for your platform. Options include SMS codes, email verification links, authentication apps, and physical tokens.
- User Education: Inform your users about the importance of MFA. A user who understands the value of an additional authentication step is more likely to embrace it without frustration.
- Seamless Integration: Ensure the MFA process is as streamlined as possible. Excessive complexity or inconvenience can deter users from completing transactions.
Data Protection through Encryption
Data protection, especially through encryption, is a critical aspect of securing any eCommerce platform. Encryption ensures that data, whether stored (data at rest) or being transmitted (data in transit), is converted into a format that is unreadable to anyone without the appropriate decryption key. This process acts as a vital safeguard, ensuring that sensitive information such as customer data, payment details, and proprietary information remains secure from unauthorized access or interception.

Understanding Encryption
- Data at Rest: Refers to all data stored on physical or virtual media. Encryption of data at rest protects against unauthorised access in case of theft or unauthorized entry into the data storage location.
- Data in Transit: Refers to data actively moving from one location to another, such as across the internet or through a private network. Encrypting this data protects it from being intercepted by attackers during transmission.
Implementing Encryption for Data Protection
Encryption of Data at Rest:
- Use Strong Encryption Standards: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with 256-bit keys is widely regarded as the gold standard for encrypting stored data.
- Encrypt Sensitive Files and Databases: Prioritize the encryption of sensitive data such as customer personal information, payment records, and login credentials.
- Manage Encryption Keys Securely: Store keys in a secure location separate from the encrypted data. Use key management best practices to rotate and manage access to keys.
Encryption of Data in Transit:
- Implement SSL/TLS Protocols: Use SSL (Secure Socket Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to encrypt data being transmitted to and from your website. This is crucial for all web traffic, especially during login and checkout processes.
- Regularly Update Protocols: Stay updated with the latest versions of SSL/TLS and other encryption protocols. Older versions may contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Use VPNs for Secure Connections: For internal data transfers or remote access, use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to ensure a secure, encrypted connection over the internet.
Best Practices for Data Encryption
- Comprehensive Encryption Strategy: Develop a comprehensive encryption strategy that covers both data at rest and data in transit. Consider the specific needs of your eCommerce platform and the sensitivity of the data you handle.
- Regularly Audit and Update Encryption Practices: Encryption standards and best practices evolve. Regularly audit your encryption practices and update them as needed to ensure you are using the most secure and efficient methods available.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure your team understands the importance of encryption and how to implement it properly. Regular training on security best practices can significantly enhance your platform's overall security posture.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Be aware of any legal or regulatory requirements regarding data protection in your jurisdiction or industry. For example, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU places specific obligations on the encryption and handling of personal data.
Regular Security Monitoring:
A Pillar of eCommerce Security
Regular security monitoring is an essential layer of defense in a comprehensive eCommerce security strategy. This process involves continuously scanning and analysing your digital environment for signs of unauthorised access, potential vulnerabilities, and other suspicious activities. By implementing a proactive and comprehensive security monitoring strategy, you can detect and mitigate threats before they escalate into serious breaches.

Why Regular Security Monitoring is Crucial?
- Early Detection of Threats: Continuous monitoring allows for the early detection of potential security threats, enabling timely intervention before any significant damage can occur.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to regulations that require continuous monitoring of sensitive data and systems. Regular security monitoring ensures compliance with these legal and regulatory obligations.
- Maintaining Customer Trust: By safeguarding customer data and maintaining the integrity of your platform, you reinforce customer trust in your brand.
- Operational Continuity: Security incidents can disrupt business operations. By identifying and addressing issues early, you ensure the smooth functioning of your eCommerce platform.
Implementing Effective Security Monitoring
- Establish a Security Operations Centre (SOC): A SOC is a centralized unit that deals with security issues on an organizational and technical level. Consider establishing a SOC that can monitor your network around the clock, using advanced tools and technologies to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
- Utilise Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IDS systems monitor network and system activities for malicious actions and policy violations. They then report these activities to administrators. IPS systems go a step further by actively preventing and blocking these intrusions.
Integrating both IDS and IPS into your environment enhances your capability to detect and respond to threats swiftly. - Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM systems provide a holistic view of an organization's information security. They work by aggregating and analysing log data from various sources within your network, identifying deviations from the norm (which could indicate a potential security issue), and alerting the security team.
- Conduct Regular Vulnerability Scans and Penetration Testing: Vulnerability Scans: Automated tools should be used to scan for software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other potential points of exploitation. Penetration Testing: Periodically employ ethical hackers to simulate cyber-attacks against your system to identify weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Train Your Staff: Ensure that your staff are trained to recognise signs of security breaches and understand the proper protocols for reporting and responding to such incidents. Human vigilance is an invaluable complement to technical monitoring tools.
Best Practices for Security Monitoring
- Customise Alerts: Configure your monitoring tools to send alerts for specific events that are most relevant to your environment, reducing the noise of non-critical alerts.
- Regularly Update Security Tools: Keep your monitoring tools up to date with the latest threat intelligence and software updates to ensure they can detect the newest threats.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Regularly review and analyse the data collected by your monitoring tools. Use this data to inform security strategy and improvements.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a clear, documented incident response plan that outlines steps to be taken when a security threat is detected.
Creating a Culture of Security Awareness
Creating a culture of security awareness within your eCommerce business is akin to building a human firewall. This approach emphasis's the critical role every team member plays in safeguarding the organisation's digital and physical assets from cyber threats. Just as technological defences are essential, fostering an environment where security is a shared responsibility can significantly enhance your overall defence against cyber-attacks.
![]()
![]()
Here's how t![]() o cultivate a robust culture of security awareness:
o cultivate a robust culture of security awareness:
- Leadership Buy-in: Security awareness must start at the top. When leaders prioritise and actively participate in security initiatives, it sets a tone for the entire organization. Leadership buy-in is crucial for allocating resources and ensuring that security awareness is woven into the fabric of the company culture.
- Develop a Comprehensive Security Awareness Program: Create a structured program that covers the critical aspects of cyber-security relevant to your business. This program should include: Onboarding Training: Introduce new hires to your security policies and expectations from day one.Regular Training Sessions: Conduct ongoing training sessions to cover new threats, refresh on best practices, and discuss any security incidents (anonymised, if necessary) that can serve as learning opportunities. Simulated Phishing Exercises: Simulate phishing attacks to teach employees how to recognize and respond to them. Use the results to guide further training.
- Make Security Awareness Engaging and Relevant: For security awareness to be effective, it must be engaging. Dull, checkbox-style training won't resonate. Use interactive e-learning courses, gamification, or even internal competitions to make learning about cyber-security interesting and relevant to employees' daily tasks.
- Encourage Open Communication Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities or potential security threats without fear of retribution. An open-door policy for reporting security concerns can be one of the most effective defences against cyber threats.
- Incorporate Security into Daily Operations: Security should not be seen as an additional task but as an integral part of daily operations. Encourage practices such as secure password management, recognizing phishing attempts, and safely handling customer data in every relevant aspect of your team's work.
- Utilise Real-world Examples: Use case studies or news stories about recent cyber-attacks to highlight the real-world implications of cyber-security. Relating abstract concepts to actual events can help underline the importance of vigilance.
- Regularly Update and Refresh Knowledge:The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and so should your team's knowledge. Regular updates about new threats, along with refreshers on your company's security policies and procedures, are essential.
- Reward and Recognise Secure Behaviors: Positive reinforcement can be a powerful motivator. Recognize and reward employees who exemplify strong security practices or who have made significant contributions to improving your organisation's security posture.
Conclusion
Our goal is to make cyber-security accessible and understandable, enabling you to confidently secure your online business against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






