What Is Red Teaming?
Red Teaming in cyber-security refers to an advanced type of ethical hacking where a group of security professionals, known as the 'Red Team', simulates realistic cyber attacks against an organisation’s environment. The primary goal is to assess and improve the effectiveness of the organisation's security controls.

Table of Contents
- What Is Red Teaming?
- What is the Purpose of Red Teaming?
- What Are The Objectives of Red Teaming?
- What Is The Red Teaming Process?
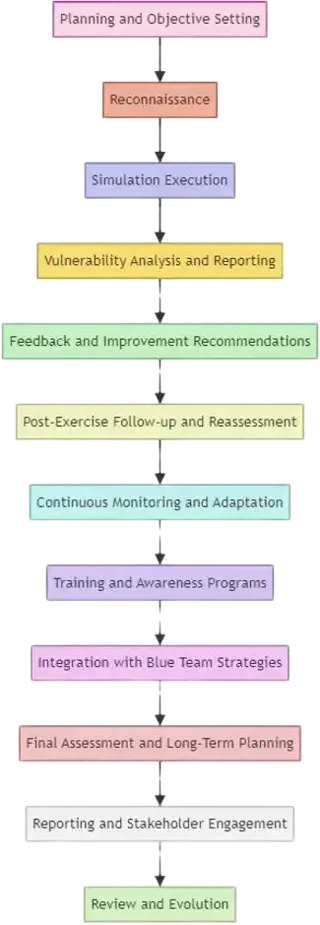
- Planning and Objective Setting
- Reconnaissance
- Simulation Execution
- Vulnerability Analysis and Reporting
- Feedback and Improvement Recommendations
- Post-Exercise Follow-up and Reassessment
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
- Training and Awareness Programs
- Integration with Blue Team Strategies
- Final Assessment and Long-Term Planning
- Reporting and Stakeholder Engagement
- Review and Evolution
- What Are The Different Red Teaming Methodologies?
- Physical Security Testing
- Social Engineering
- Network Penetration Testing
- Application Security Testing
- Wireless Security Testing
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Simulation
- Insider Threat Simulation
- Supply Chain and Third-Party Risk Assessment
- Crisis Management and Response Testing
- Physical Intrusion and Environmental Controls Testing
- Compliance and Policy Adherence Testing
- Customised Scenario Development
- What Are The Benefits of Red Teaming?
- What Are The Challenges in Red Teaming?
- What Are The Red Teaming Best Practices?
- What Is The Future of Red Teaming?
- What Is Red Teaming in Various Industries
- What Are Ethical Considerations in Red Teaming?
- What Are Training and Certification for Red Teams?
- Common Questions
What is the Purpose of Red Teaming?
Red teaming is employed in cyber security to test an organisation's defenses by simulating realistic cyber attacks. Its core purpose is to uncover vulnerabilities in security environments that might not be evident through other forms of security testing. By adopting the perspective of attackers, Red Teaming provides a rigorous examination of security measures, protocols, and responses to ensure that an organisation can effectively withstand sophisticated cyber assaults.
This proactive security practice helps organisations:
- Validate the effectiveness of their current security measures and protocols.
- Assess the responsiveness of their incident response teams.
- Educate and train employees in recognizing and responding to potential security threats.
- Enhance their overall security posture by identifying and addressing gaps before actual attackers can exploit them.
- Foster a culture of continuous security improvement and vigilance against emerging threats
Red teaming goes beyond conventional security testing by incorporating a multi-faceted approach that evaluates not just technical defenses, but also physical security and human factors. This holistic assessment helps ensure that the organization can defend against and respond to a wide range of security challenges.
What Are The Objectives of Red Teaming?
The primary objectives of Red Teaming include:-
- Identifying Security Vulnerabilities: The systematic uncovering of vulnerabilities within an organisation's cyber-security defenses. This encompasses an analysis of networks, applications, physical security parameters, and human factors to identify any potential vulnerabilities.
- Evaluation of Response Capabilities: This aspect of Red Teaming is concerned with the organisation’s capacity to detect and counteract cyber-attacks. It involves thorough assessment of the incident response protocols to determine their efficacy and ability to respond to real-time scenarios.
- Staff Training and Awareness: Red Teaming serves as a practical framework for educating organisational staff. By simulating cyber-attack scenarios, it enhances staff awareness regarding security practices, potential threats, and the formulation of appropriate responses.
- Validating Security Measures: An integral objective of Red Teaming is to affirm the effectiveness of existing security policies and measures. It ensures that the implemented strategies are competent in mitigating real-world cyber threats
- Developing a Proactive Security Mindset: Red Teaming promotes a transition from a reactive to a proactive stance in cyber-security. It underscores the importance of continuous improvement and the proactive anticipation of emerging threats.
What Is The Red Teaming Process?
Understanding the Red Teaming process is paramount for organisations endeavoring to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. This process encompasses a sequence of steps, each purposed to rigorously evaluate and subsequently enhance the defensive mechanisms of an entity..

Planning and Objective Setting
The initial stage involves the Red Team delineating precise objectives for the exercise. This phase is characterised by the identification of specific areas to test, encompassing network security, physical security, and personnel awareness.
Reconnaissance
This phase entails the Red Team in gathering pertinent information regarding the target organisation. It involves the collection of public data, network footprints, and personnel details to prepare for the simulation execution.
Simulation Execution
During this stage, the Red Team executes the attack scenarios that were planned. This might manifest in attempts to breach physical defenses, initiate cyber-attacks, or execute social engineering campaigns.
Vulnerability Analysis and Reporting
Subsequent to the simulation, this phase involves the analysis of the outcomes, pinpointing vulnerabilities that were exploited and evaluating the resilience of the organisation’s defenses.
Feedback and Improvement Recommendations
This stage is dedicated to providing the organisation with comprehensive feedback and recommendations. It focuses on outlining remedial actions for the identified vulnerabilities and proposing strategies to increase overall security.
Post-Exercise Follow-up and Reassessment
After the implementation of recommended fixes/changes by the organisation, this phase involves a reassessment to verify that the vulnerabilities have been fixed and to evaluate the effectiveness of the improvements made.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Beyond the post-exercise assessment, this stage emphasises the necessity for continuing vigilance. The Red Team may engages in ongoing surveillance to ensure the durability of the security improvements made and their adaptability to emergent threats.
Training and Awareness Programs
Integral to the Red Teaming methodology, this phase aims at educating the organisation’s personnel. It involves the execution of staff awareness programs to educate employees about security best practices and response strategies to potential threats.
Integration with Blue Team Strategies
This phase underscores the collaboration between the Red Team (offensive) and Blue Team (defensive), aiming at integrating Red Team insights into the organisation’s defense strategies.
Final Assessment and Long-Term Planning
Concluding the process, this stage involves an evaluation of the long-term implications of the Red Teaming exercise. It is pivotal for the organisation to formulate a long term plan to evolve its security stance in alignment with emerging threats.
Reporting and Stakeholder Engagement
Essential to the process, this stage involves the dissemination of detailed reports to stakeholders, ensuring that executive leadership is aware of the organisations cyber-security posture and the value of Red Teaming.
Review and Evolution
Acknowledging the dynamic nature of cyber-security threats,, with the Red Teaming process evolving based on new threats, this final stage advocates for the continual reassessment and evolution of the Red Teaming process to maintain its relevance and effectiveness.
What Are The Different Red Teaming Methodologies?
The various methodologies employed during a Red Teaming exercise are diverse and tailored to thoroughly test the organisation’s defence mechanisms used. This section outlines the various Red Teaming methodologies used, each meticulously designed to evaluate and fortify various aspects of an organisation's cyber-security environment. The following list provides details each of these methodologies, whilst emphasising their significance in contemporary cyber-security practices.
Physical Security Testing
This entails a thorough assessment of an organisation's physical security controls, this methodology includes, but is not limited to, access controls, surveillance systems, and alarm mechanisms. The objective is to identify any vulnerabilities that could be exploited to gain unauthorised physical access to secure premises.

Social engineering
This methodology examines the susceptibility of an organisation's personnel to social engineering tactics such as phishing, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating. The aim is to evaluate the robustness of the human element in the cyber-security equation, focusing on the potential for individuals to inadvertently compromise security protocols.
Network Penetration Testing
Focusing on the digital infrastructure, this methodology seeks to identify and exploit vulnerabilities within an organisation's network. Key components such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other network defence measures are subjected to rigorous testing to assess their efficacy in preventing cyber attacks.
Application Security Testing
This aspect of Red Teaming involves the critical analysis of software applications by identifying and exploiting security flaws in the code, authentication processes, and integration with third-party services. The goal is to ensure that software applications are properly fortified against potential cyber threats.
Wireless Security Testing
This approach involves evaluating the security of wireless communication protocols, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and NFC, are tested for vulnerabilities. The objective is to identify vulnerabilities that could facilitate unauthorised access to data or data interception.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Simulation
This methodology simulates the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of advanced threat actors, including nation-states and sophisticated criminal organisations. It tests an organisation's resilience against prolonged and stealthy cyber attack campaigns.
Insider Threat Simulation
Recognising the potential for threats originating from within the organisation, this approach simulates actions by malicious insiders to evaluate the resilience of internal security measures and identify potential vulnerabilities.

Supply Chain and Third-Party Risk Assessment
This methodology involves the evaluation of security risks associated with third-party vendors and supply chains, assessing how external entities could potentially compromised to breach organisational security.
Crisis Management and Response Testing
Through the simulation of crisis scenarios, this methodology assesses an organisation's preparedness and response capabilities in the face of significant cyber-security incidents.
Physical Intrusion and Environmental Controls Testing
Beyond direct physical attacks, this approach evaluates the effectiveness of physical intrusion methods and environmental control systems in safeguarding organisational assets.
Compliance and Policy Adherence Testing
This methodology measures an organisation's compliance with the relevant cyber-security standards and internal policies, ensuring compliance with the regulatory and policy requirements.
Customised Scenario Development
Tailoring scenarios to the specific context and vulnerabilities of an organisation allows for a targeted and relevant evaluation of cyber-security defenses.
What Are The Benefits of Red Teaming?
Red Teaming exercises are an invaluable part of a organisations cyber-security strategy. They offer numerous benefits that help organizations fortify their defenses against cyber threats.

The key benefits include:
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Red Teaming provides a realistic and holistic assessment of an organization's vulnerabilities, including those that may be overlooked in standard security evaluations.
- Enhanced Security Posture: The insights gained from Red Teaming exercises lead to stronger security measures, helping organizations develop a more robust defense against cyber attacks.
- Real-World Testing of Policies and Procedures: Red Teaming tests an organization's policies and incident response procedures in real-world scenarios, ensuring they are effective under actual attack conditions.
- Improved Employee Awareness and Response: These exercises enhance employee awareness about cyber-security, improving their ability to recognize and respond to real cyber threats.
- Validation of Security Investments:Red Teaming helps validate the effectiveness of security investments, demonstrating the value of cyber-security measures to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Preparation for Evolving Threats: Regular Red Teaming exercises prepare organizations to face evolving cyber threats, fostering agility and adaptability in their cyber-security strategies.
What Are The Challenges in Red Teaming?
While Red Teaming is an effective tool in cyber-security, it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for conducting successful and responsible Red Teaming exercises.
- Balancing Realism with Safety: Ensuring the Red Teaming exercises are realistic yet do not endanger the organization's operations or compromise sensitive data

- Legal and Ethical Constraints: Navigating the legal and ethical boundaries, especially when employing tactics like social engineering or physical penetration testing.
- Resource and Time Intensiveness: Red Teaming exercises can be resource-intensive, requiring significant time, expertise, and tools, which can be challenging for organizations with limited resources.
- Managing Organizational Impact: Minimizing the disruption to regular business processes while conducting thorough testing can be a delicate balance to achieve.
- Keeping Pace with Evolving Threats: Continuously updating tactics and techniques to stay ahead of rapidly evolving cyber-security threats and attacker methodologies.
- Measuring Success and ROI: Effectively measuring the success of Red Teaming exercises and demonstrating a return on investment can be challenging, especially when quantifying intangible benefits like improved awareness.

What Are The Red Teaming Best Practices?
Adhering to best practices in Red Teaming is crucial for ensuring the exercises are effective, ethical, and yield valuable insights.
Here are key best practices to follow:
- Clear Scope and Objectives: Define clear objectives and scope for the Red Teaming exercise, including what is off-limits, to ensure focused and relevant testing.
- Obtain Necessary Approvals and Legal Compliance: Ensure all Red Teaming activities are approved by top management and comply with legal and ethical standards.
- Use of Multidisciplinary Teams: Engage a diverse team with varied skills, including cyber-security, physical security, and social engineering, to cover all aspects of the organization’s vulnerabilities.

- Realistic but Safe Simulation: Ensure that the simulations are realistic but do not pose any real threat to the organization’s data, employees, or operations.
- Comprehensive Debriefing and Feedback:Conduct thorough debriefing sessions post-exercise to discuss findings, provide feedback, and develop improvement strategies.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the insights gained from Red Teaming exercises to continuously improve security measures and regularly update Red Teaming strategies.

What Is The Future of Red Teaming?
The future of Red Teaming is dynamic, with an increasing focus on adapting to emerging technologies like AI and machine learning.
Future trends may include:
- Integration of Advanced Technologies:The future of Red Teaming will likely see increased integration of advanced technologies like multi-agent artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automated systems to create more sophisticated and realistic attack simulations.

- Emphasis on Multi-Dimensional Threats:Future Red Teaming exercises are expected to address multi-dimensional threats that combine cyber with physical and social engineering attacks, providing a more
- Increased Focus on Cyber-Physical Systems: As the inter connectivity between digital and physical systems grows, Red Teaming will expand its focus to include cyber-physical systems, particularly in critical infrastructure.
- Collaboration with AI for Threat Modeling: Utilizing AI to assist in complex threat modeling and scenario generation, making Red Teaming exercises more dynamic and unpredictable.
- Global Collaboration and Information Sharing: There will likely be an increase in global collaboration and information sharing among Red Teams, leading to a more unified approach to understanding and combating
- Adaptive and Continuous Learning Systems: Red Teaming tools and methodologies will likely become more adaptive, utilizing continuous learning systems to evolve tactics based on new data, trends, and past exercise outcomes.

What Is Red Teaming in Various Industries?
Red Teaming is a versatile practice that can be adapted to the unique security needs of different industries. Each sector faces its own set of challenges, which Red Teaming exercises can help to identify and mitigate.

- Financial Services: In the financial sector, Red Teaming is crucial for protecting sensitive financial data and transaction systems. The focus is often on preventing data breaches, fraud, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
- Healthcare: Red Teaming in healthcare focuses on protecting patient information, ensuring the integrity of medical records, and securing connected medical devices.
- Retail and E-Commerce: For retail and e-commerce, Red Teaming helps secure online transactions, protect customer data, and prevent service disruptions.
- Government and Public Sector: In government sectors, Red Teaming is used to protect sensitive national data, guard against espionage, and secure public infrastructure.
- Manufacturing and Industrial: Red Teaming in manufacturing focuses on protecting industrial control systems, securing supply chains, and preventing disruptions in production.
- Technology and Telecommunications: This sector requires Red Teaming to secure networks, protect intellectual property, and ensure the integrity of communication systems.
- Education: In educational institutions, Red Teaming is important for protecting student data, securing research information, and ensuring the safety of digital learning platforms.
- Energy and Utilities: Red Teaming in this sector focuses on securing critical infrastructure like power grids, water treatment facilities, and ensuring the resilience of energy supply chains.
- Transportation and Logistics: Here, Red Teaming helps to protect logistics data, secure transportation networks, and prevent disruptions in supply chains.
- Hospitality and Entertainment: In these industries, Red Teaming is used to secure booking systems, protect customer data, and ensure the safety of online entertainment platforms.
- Legal and Consulting Services: For legal and consulting firms, Red Teaming is crucial for protecting sensitive client information, maintaining confidentiality, and ensuring the integrity of legal documents.
- Non-Profit and NGO Sector: Non-profits and NGOs use Red Teaming to protect donor information, secure communication channels, and safeguard sensitive mission data.
What Are Ethical Considerations in Red Teaming?
Ethical considerations are paramount in Red Teaming exercises to ensure that these simulated attacks are conducted responsibly and do not cause unintended harm or legal issues.
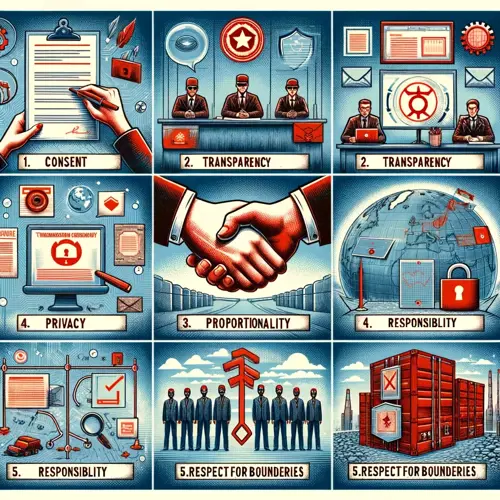
Here are key ethical aspects to consider:
- Consent and Authorization: It's crucial to obtain explicit consent and proper authorization from all relevant stakeholders before commencing a Red Teaming exercise. This ensures that all activities are legally and ethically sanctioned.
- Proportionality of Actions: Red Teaming activities should be proportional to the objectives and should not exceed the scope of what is necessary to test the security systems effectively.
- Respect for Privacy: Red Teaming must respect individual privacy and confidentiality. Any personal data encountered during simulations should be handled in accordance with privacy laws and organizational policies.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Disruption: While testing the organization's defenses, efforts should be made to avoid unnecessary disruption to regular business operations or employee productivity.
- Transparency and Reporting: After the exercise, provide transparent reporting on the actions taken, vulnerabilities found, and recommendations for improvement. This helps build trust and understanding of the Red Teaming process
What Are Training and Certification for Red Teams?
In the UK, there are several pathways for individuals looking to specialize in Red Teaming.

These include professional training programs, certifications, and educational courses designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills.
- Professional Certification Programs: Various organizations offer certifications specific to Red Teaming. Popular certifications include , CREST Certified Tester (CCT), and CREST Certified Simulated Attack Specialist (CSAS)
- University Courses and Degrees: Several UK universities offer courses and degree programs in cyber-security, ethical hacking, and information security, providing a strong academic foundation for aspiring Red Team members.
- Specialized Training Providers: There are numerous training providers offering specialized courses in Red Teaming, penetration testing, and ethical hacking. These courses are often practical and scenario-based, providing hands-on experience.
- Online Learning Platforms: Online platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and Cybrary offer courses on Red Teaming and related fields, making it accessible for individuals to learn remotely.
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular workshops, seminars, and conferences on cyber-security and Red Teaming are held in the UK. These events provide opportunities for networking and learning from experienced professionals.
Common Questions
Red Teaming is a complex field with many facets. Here are some commonly asked questions to help demystify Red Teaming and provide clarity on its purpose and execution.
1. What is Red Teaming in Cyber-security?
Answer: Red Teaming is a practice in cyber-security where a team of experts simulate realistic cyber attacks on an organization to test and improve its defenses. It’s like a real-world security drill, probing for vulnerabilities and testing the effectiveness of security measures.
2. How Does Red Teaming Differ from Penetration Testing?
Answer: While penetration testing focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in a system, Red Teaming provides a more comprehensive approach by simulating real-life cyber attacks to test not just the digital defenses, but also physical and human security measures.
3. What is Blue Teaming?
Answer: Blue Teaming involves the organisation's internal security team, known as the "Blue Team," whose role is focused on defending against the Red Team's attacks. The Blue Team's responsibilities include maintaining daily security protocols, detecting breaches, responding to incidents, and recovering from attacks. Their ongoing task is to fortify the organization's defenses and minimize the impact of any actual breaches.s
4. Who Should Consider Red Teaming?
Answer: Any organisation that wants to rigorously test its security measures should consider Red Teaming. It is particularly beneficial for industries with high-stakes data and assets, such as finance, healthcare, government, and technology sectors.
5. What Skills are Required for a Red Team Member?
Answer: Red Team members typically need a mix of technical skills in cyber-security, knowledge of network systems, proficiency in penetration testing tools, and often, skills in social engineering. Creative thinking and problem-solving are also crucial.
6. How Often Should Red Teaming Exercises Be Conducted?
Answer: The frequency of Red Teaming exercises depends on various factors, including the organization’s size, nature of data handled, and changes in the threat landscape. Generally, conducting these exercises annually or bi-annually is advisable.
7. What are the Ethical Considerations in Red Teaming?
Answer: Ethical considerations include obtaining proper authorization, respecting privacy, ensuring activities are legal and within scope, and avoiding unnecessary disruption to business operations.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






