What is Phishing? Understanding and Protecting Against Email Scams
Phishing involves sending fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable source, usually through email. The goal is to steal sensitive data or deploy malicious software.
This comprehensive guide explores phishing in detail, discussing its various types, the mechanics of phishing attacks, and how individuals and organizations can protect themselves.
How Phishing Works:
- Attackers send out a large number of fraudulent messages: with the aim of capturing sensitive information.They design emails to look like they come from trusted sources, such as financial institutions, tech companies, or colleagues.
- Execution:The phishing email contains a call to action, such as clicking on a link or downloading an attachment.Once the action is taken, it can lead to the installation of malware or direct users to a fake website to collect personal information.
Types of Phishing
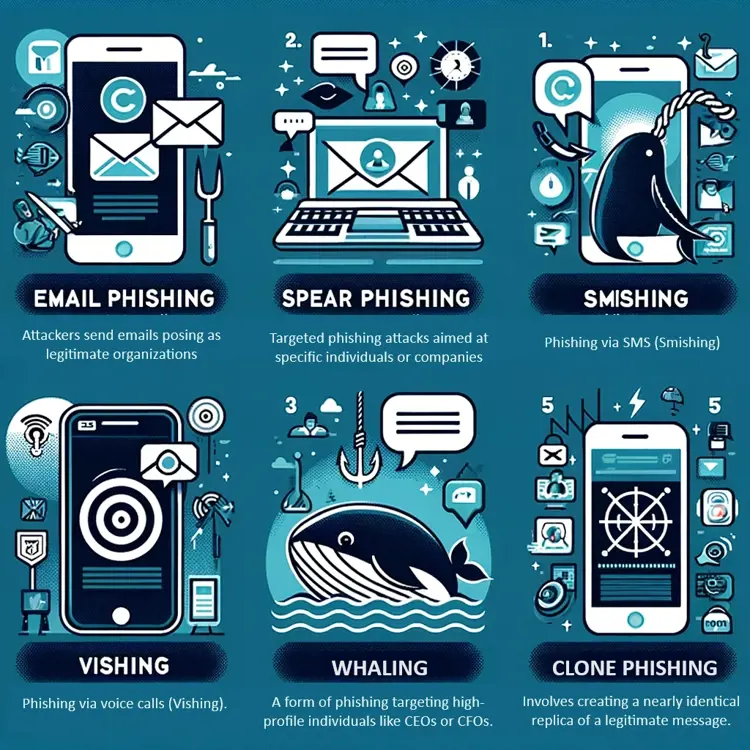
Email Phishing:
- Definition: The most common form of phishing, where attackers send emails posing as legitimate organizations.
- Characteristics: Generic greetings, urgent or threatening language to prompt immediate action.
- Prevention Tips: Verify the sender's email address, look for spelling errors, and avoid clicking on unsolicited links.
Spear Phishing:
- Definition: Targeted phishing attacks aimed at specific individuals or companies.
- Characteristics: Personalized information, often gathered through social engineering.
- Prevention Tips: Be cautious of emails asking for confidential information, even if they seem to come from known contacts.
Smishing and Vishing:
- Definition: Phishing via SMS (Smishing) or voice calls (Vishing).
- Characteristics: Text messages or calls that create a sense of urgency to divulge personal information.
- Prevention Tips: Never share personal information over text or phone calls from unknown numbers.
Whaling:
- Definition: A form of phishing targeting high-profile individuals like CEOs or CFOs.
- Characteristics: Often involves legal or financial content to manipulate the target into transferring funds or revealing sensitive information.
- Prevention Tips: Use multi-factor authentication and conduct regular security training for senior staff.
Clone Phishing:
- Definition: Involves creating a nearly identical replica of a legitimate message.
- Characteristics: A cloned email with malicious links, replacing the original links.
- Prevention Tips: Double-check emails for authenticity, especially those with links or attachments.
Common phishing tactics:
- Domain Spoofing: The creation of fake websites or email addresses that mimic legitimate ones to deceive victims.
- Link Manipulation: Embedding malicious links in seemingly benign emails or messages, leading to fraudulent websites.
- Social Engineering: Exploiting human psychology to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing certain actions.
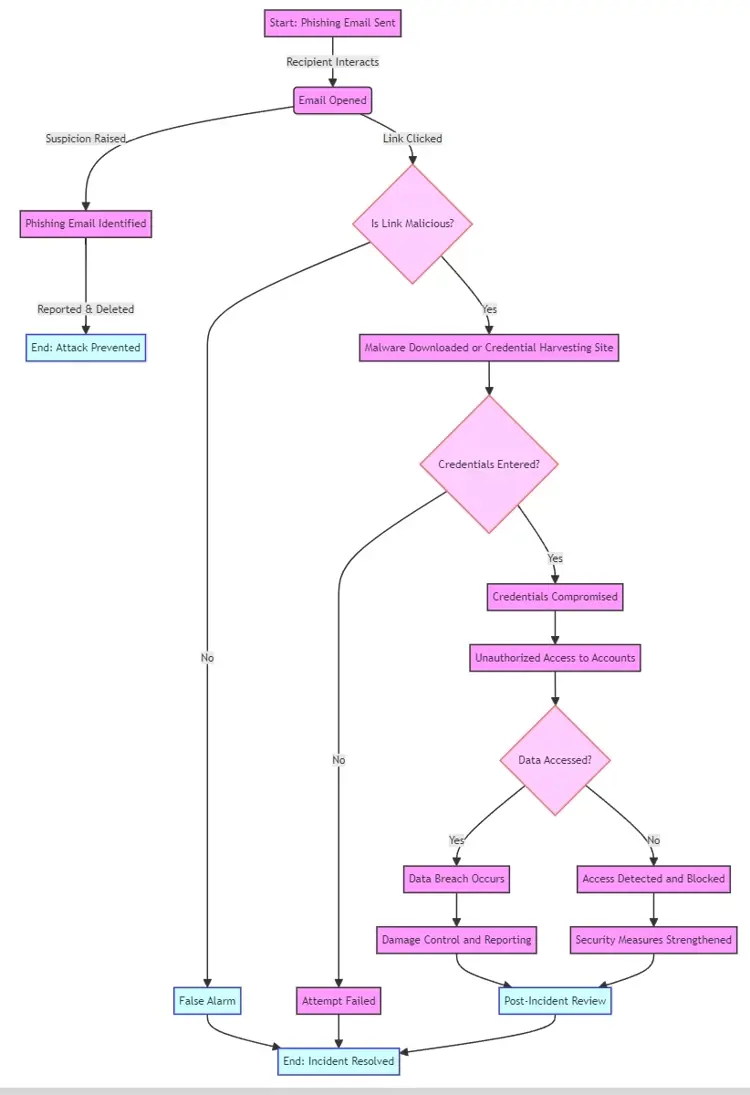
Phishing Flowchart
Evolution and future trends in phishing
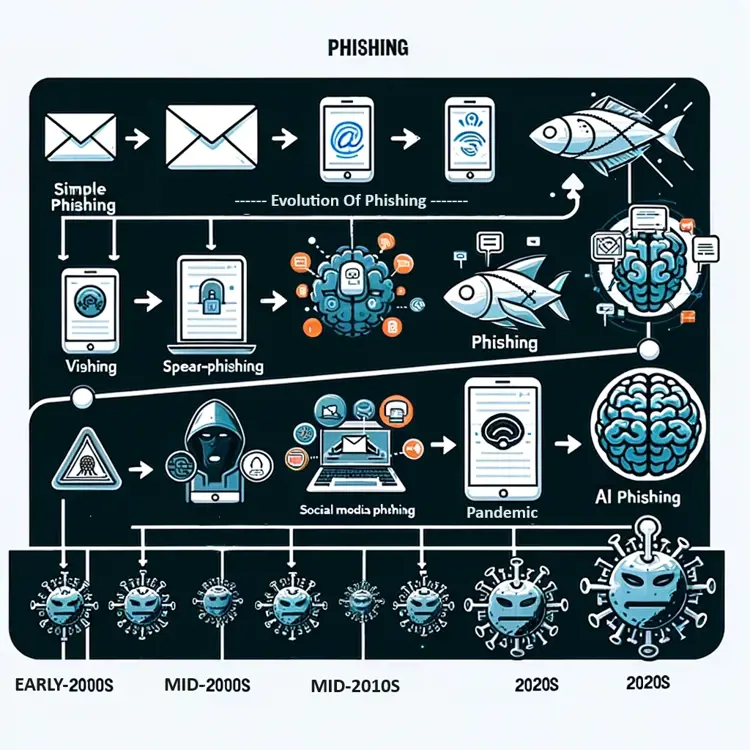
Recent Trends in Phishing:
- Mobile Phishing: Rise in phishing attacks targeting mobile devices due to increased smartphone usage.
- Social Media Phishing: Utilization of social media platforms for phishing, exploiting the trust in these networks.
- IoT and Phishing: Potential phishing risks associated with the increasing use of IoT devices.

Latest Trends in Phishing:
- Rise in COVID-19 Related Scams: Attackers are exploiting the pandemic to trick users with fake health updates or donation requests.
- Sophistication in Social Engineering: Increasingly convincing phishing attempts using detailed personal information.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence: AI is being utilized to create more believable phishing content and automate attacks.
Future Trends in Phishing:
- Advanced Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks using sophisticated methods to deceive specific individuals or organizations.
- AI-Generated Phishing Content: The use of artificial intelligence to create more convincing phishing emails and messages.
- Rise of Voice Phishing (Vishing): Increasing use of phone calls for phishing, exploiting the less guarded nature of verbal communication.
Impact of Phishing
- Financial Losses: Phishing can lead to significant financial damages for both individuals and organizations.
- Data Breaches: Sensitive personal and corporate data can be exposed or stolen.
- Reputational Damage: Businesses can suffer long-term reputational harm, affecting customer trust and corporate partnerships.
Impact of Phishing on Different Sectors:
- Financial Sector: The high cost of phishing in terms of financial loss and reputational damage.
- Healthcare: The threat to patient data and critical healthcare systems.
- Government and Public Sector: The risk to national security and public services.
Preventing Phishing
Phishing Preventive Technologies:
- Email Authentication Protocols: Implementation of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent email spoofing.
- Phishing Detection Software: Tools that use machine learning algorithms to detect and alert users of phishing attempts.
- Secure Email Gateways: Filtering incoming emails to block phishing and other malicious emails.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA to provide an additional layer of security against phishing attacks.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping all software, including anti-phishing tools, up-to-date to combat the latest phishing threats.
Phishing Preventive Strategies:
Individual Level:
- Awareness: Recognize the signs of phishing and stay updated on new phishing methods.
- Security Measures: Use antivirus software, keep systems updated, and use strong, unique passwords.
Organisational Level:
- Employee Training: Regular training sessions for employees to recognize and avoid phishing attempts.
- Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to keep phishing risks and prevention strategies in the public eye.
- Simulated Phishing Exercises: Conducting controlled phishing attacks to test employee vigilance and training effectiveness.
- Email Filters: Implement advanced email filtering solutions to detect and block phishing attempts.
- Incident Response Planning: Having a well-defined plan to respond quickly and effectively to phishing incidents.
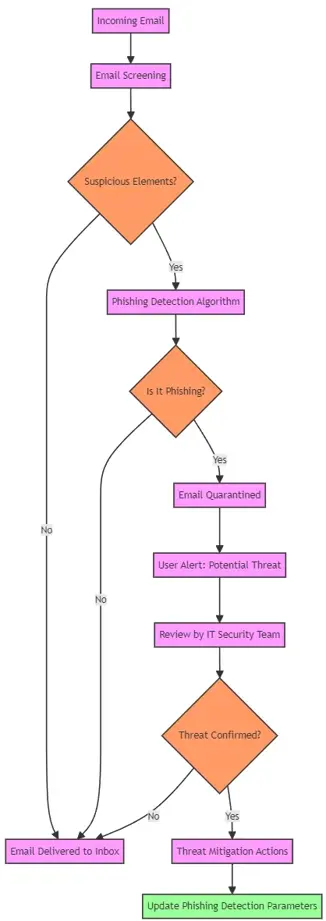
Email Screening Flowchart
Legislation and Compliance
- GDPR and Data Protection: Underlines the importance of protecting personal data, which includes measures against phishing.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Certain sectors, like finance and healthcare, have additional compliance requirements that cover phishing defenses.
Reporting and Responding to Phishing
- Internal Reporting Mechanisms: Establishing clear protocols within organizations for employees to report suspected phishing attempts.
- External Reporting: Encouraging the reporting of phishing attempts to relevant authorities or cybersecurity organizations.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a comprehensive plan to respond to confirmed phishing attacks, including steps to mitigate damage and prevent future occurrences.
Conclusion
Understanding and combating phishing is vital in today's digital landscape. By staying informed about the latest phishing tactics and implementing robust defenses, individuals and organisations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these attacks.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






