Edge Testing
In the digital realm where technologies are continuously evolving, ensuring security has sprawled beyond the conventional methodologies. Edge Testing becomes a focal point in cyber security, ensuring the perimeter devices, IoT gadgets, and distributed networks retain their robustness against potential cyber threats.

Definition
Edge Testing refers to a comprehensive testing strategy that involves examining the security, performance, and reliability of applications, networks, and services that are delivered from the edge of the internet. In the context of cyber-security, it represents a pivotal approach that primarily focuses on safeguarding data by meticulously testing the devices and technologies positioned on the ‘edge’ of your network - be it IoT devices, routers, or other peripherals that are susceptible to external threats.
Understanding the Importance of Edge Testing
Navigating through the exponentially growing web of interconnected devices and networks, the aspects of cybersecurity have widened their horizons. Edge Testing is not merely a testing approach but a comprehensive strategy that ensures every nodal point of your digital network is resilient against cyber-attacks. From safeguarding IoT devices to securing data transmission across a vast network - Edge Testing enacts as a vigilant sentinel, ensuring data integrity and safeguarding user privacy.
It is quintessential to understand that with the proliferation of IoT devices and the burgeoning reliance on cloud technologies, the traditional centralized data-processing model is gradually shifting towards a decentralized model. This shift propagates the necessity of implementing a meticulous and robust Edge Testing strategy.

The Methodology Behind Edge Testing
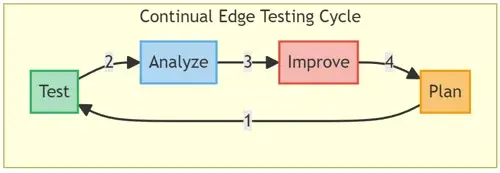
Understanding the methodology behind Edge Testing is pivotal in comprehending how it enhances the cyber-security posture of an entity. This segment delineates the systematic, structured, and strategic approach towards conducting edge testing.
Stage 1: Mapping the Edge Network
Identifying and documenting all the edge devices and nodes, understanding their interactions, and recognizing the potential data flow paths within the network.
Stage 2: Formulating Test Scenarios
Upon mapping the edge network, the subsequent step involves devising diverse test scenarios that envisage potential cyber-attack vectors and system failures. This encompasses scrutinizing various elements like data transmission, device integrity, and secure communication within the network.
Stage 3: Execution of Test Scenarios
The test scenarios are meticulously executed under a controlled environment, mimicking the potential threats and vulnerabilities. This phase is pivotal for identifying unforeseen vulnerabilities and understanding the robustness of the edge network against potential cyber threats.
Stage 4: Analysis and Optimization
Post-execution, a thorough analysis is conducted to derive insights from the test results. It essentially involves interpreting the data, identifying vulnerabilities, and understanding their implications. The insights gained are employed to optimize and enhance the security framework of the edge network.

Challenges In Edge Testing
Navigating through the sophisticated realm of edge testing entails various challenges such as:
- Network Complexity: Managing and ensuring the security of a complex network comprised of diverse IoT devices and technologies.
- Data Security: Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted across the edge network.
- Device Diversity: Managing and securing a wide spectrum of devices with varying operating systems, configurations, and security protocols.

Strategies to Overcome Challenges in Edge Testing
Handling the complexity and ensuring optimal security within edge networks require adept strategies and solutions that specifically cater to the challenges witnessed during edge testing.
1. Adaptive Security Protocols:
Implementing adaptive and robust security protocols that are capable of safeguarding varied devices within the network, irrespective of their operating system or configuration.

2. Data Encryption:
Leveraging state-of-the-art encryption methodologies for protecting data throughout its lifecycle, from creation and transit to storage, ensuring no unauthorized access or data leakage.

3. Network Segmentation:
Implementing network segmentation to create secured, isolated segments within the network, reducing the risk of widespread network vulnerability exploitation.
Real-World Application of Edge Testing
The profoundness and applicability of edge testing become particularly pronounced when observed through the lens of real-world scenarios.
- Healthcare IoT: With the integration of IoT devices in healthcare, ensuring secure communication between wearable devices, medical apparatus, and central servers is pivotal. Edge testing ascertains that data, such as patient vitals and records, are securely transmitted and stored, safeguarding against potential cyber-security threats.
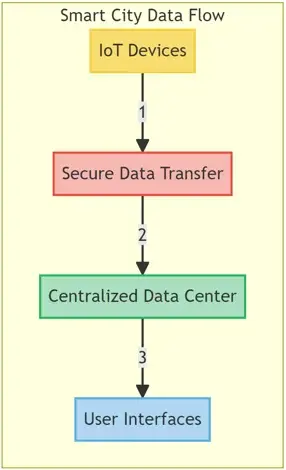
- Smart Cities: Edge testing ensures the security of smart infrastructure, such as traffic control systems, smart grids, and public surveillance systems, by scrutinizing the network and validating secure data transmission, storage, and processing.

Case Studies: The Efficacy Of Edge Testing
Case Study 1: Securing Smart Healthcare Devices
A health-tech company, specializing in developing smart healthcare devices for remote patient monitoring, leveraged edge testing to navigate through the convolutions of data security and network integrity. Edge testing was instrumental in detecting vulnerabilities within the data transmission channels and ensuring the encrypted storage of sensitive patient data, thereby preserving the sanctity of patient confidentiality and adhering to healthcare compliance.

Case Study 2: Fortifying Smart City Infrastructures
In a project aimed at implementing smart city infrastructure, a municipality faced the challenge of ensuring secure data flow among numerous IoT devices, centralized data centers, and user interfaces. Edge testing provided a framework for evaluating the robustness of data security protocols and ensured that user data generated from various sources like surveillance cameras, traffic management systems, and utility management were not susceptible to unauthorized access or cyber-attacks.
Trends And Advancements In Edge Testing
As technology continues to evolve, edge testing adapts and morphs, presenting the following trends:
- Automated Edge Testing: The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to create automated testing protocols, reducing manual intervention, and enhancing testing efficiency.
- 5G Technology: With the rollout of 5G, edge testing will need to adapt to higher data speeds and increased data volumes, ensuring security without compromising performance.
- IoT Security: As IoT devices burgeon, developing scalable and robust testing frameworks to ensure the security of an increasingly connected world becomes paramount.

The Way Forward: Preparing for Future Security Challenges
Staying vigilant and continuously updating testing methodologies is crucial in order to remain one step ahead of potential cyber-security threats. Your journey towards fortifying your edge network and ensuring the secured operability of your devices and data starts with comprehensive edge testing.
Exploring Edge Testing Tools and Methodologies
In an era where data leaks and cyberattacks have become increasingly prevalent, the methodology and tools utilized for edge testing play a pivotal role in safeguarding data and ensuring uninterrupted functionality of IoT devices and networks. Here, we delve deeper into some of the primary tools and methodologies adhered to in the realm of edge testing.

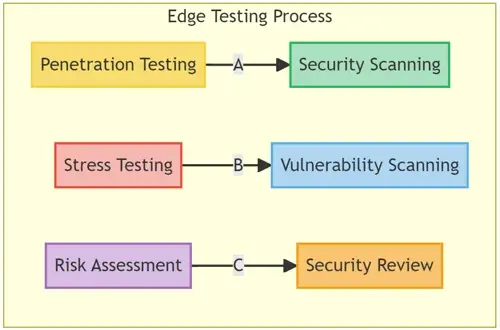
- Penetration Testing: A simulated cyberattack against your computer system to check for exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Stress Testing: Involves testing an application under extreme workloads to see how it handles high traffic or data processing.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Automated process of proactively identifying network, application, and system vulnerabilities.
- Risk Assessment: Involves analysis of security risks observed in the organization and plans for mitigating those risks.
- Security Review: A holistic review of an application’s security, ensuring all aspects, from code to functionality, meet security benchmarks.
Tool Spotlight: Edge Testing Solutions
- Wireshark: A widely-used network protocol analyzer that provides a meticulous breakdown of your network traffic.
- Nmap: An open-source tool for network exploration and security auditing.
- Metasploit: A penetration testing platform that helps you validate your defenses.
- OpenVAS: A software framework of several services and tools offering vulnerability scanning and management.
- Nessus: One of the most popular vulnerability scanners in the world.
Addressing Challenges and Building Resilient Systems
While edge testing provides a robust framework to safeguard against various cyber threats, it is not devoid of challenges:
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that the data remains unaltered during transmission and storage.
- Real-Time Challenges: Handling and analyzing data in real-time with minimal latency.
- Scalability: Managing the increased load without compromising data security.

Conclusion:
Navigating the Future with Secure Edges
Edge testing stands pivotal in protecting IoT devices and networks, especially in environments laden with interconnected devices and heavy data exchange. As technologies evolve, so do cyber threats, making it imperative for organizations to continuously enhance their edge testing strategies to safeguard against potential risks. Through the judicious application of methodologies and tools, organizations can navigate through the digital landscape with robust security mechanisms.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






