What is Cyber Security? Definition & Best Practices
Cyber Security, at its core, entails the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect digital assets, networks, and data from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and damage. As our reliance on digital platforms grows, so does the importance of robust cyber security measures to ensure the safety and integrity of our digital interactions and data.
The Pillars of Cyber Security
Cyber Security is built upon three fundamental pillars, often referred to as the CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.

Confidentiality:Ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity:Guaranteeing that data is accurate and unchanged, free from unauthorized alterations.
Availability:Making sure that systems and data are available when needed.
Importance of Cyber Security
In an era where data breaches and cyber attacks are commonplace, cyber security is indispensable for individuals, enterprises, and nations. It protects against financial losses, safeguarding of sensitive data, and upholding of reputation.
Types of Cyber Threats
Understanding the vast array of cyber threats is the first step towards developing a robust security strategy.
- Malware: Malicious software designed to cause harm, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information, like usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Unauthorized interception and possible alteration of communication between two parties.
Cyber Security Best Practices
Adopting best practices in cyber security can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keeping software and systems updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhancing authentication processes to prevent unauthorized access.

Implementing a Cyber Security Framework
A structured cyber security framework aids in managing and mitigating risks effectively.
- Identify: Recognize the assets and systems that need protection.
- Protect: Implement measures to safeguard these assets.
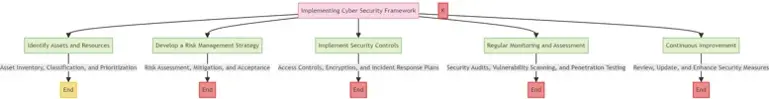
This structured layout offers a foundational understanding of cyber security, covering its definition, importance, types of cyber threats, best practices, and the implementation of a cyber security framework. The mid-journey prompts for images and flowcharts provide opportunities to visually illustrate complex concepts, making the page engaging and informative.
Advanced Cyber Security Measures
As cyber threats evolve, so must the measures to counteract them. Advanced cyber security measures include a blend of cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to stay ahead of potential threats.
- Threat Intelligence:Gathering and analyzing information about emerging threats to stay one step ahead of cyber adversaries.
- Indicator of Compromise (IoC): Identifying signs that may indicate a breach.
- Incident Response:Preparing for and reacting to security incidents to minimize damage and recover swiftly.
- Incident Response Plan (IRP): Having a well-defined plan to tackle security incidents.
- Security Automation and Orchestration:Utilizing automation tools to streamline security operations and respond to threats faster.
- Automated Threat Detection: Employing automated tools for real-time threat detection.
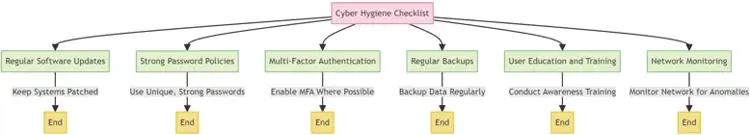
Cyber Hygiene
Maintaining good cyber hygiene is fundamental to a robust cyber security posture.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- User Awareness Training: Educating users about security best practices and potential threats.
Cyber Security Compliance and Regulations
Adhering to compliance standards and regulations is crucial for not only staying lawful but also for ensuring robust security.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Adhering to data protection standards in the European Union.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of healthcare information.
Tools and Technologies
Leveraging the right tools and technologies is pivotal for an effective cyber security strategy.
- Firewalls: Employing firewalls to block unauthorized access.
- Encryption Tools: Utilizing encryption to protect data during transit and at rest.

Conclusion
Understanding and implementing cyber security measures is imperative in the digital age. From recognizing the importance of cyber security, identifying various cyber threats, to adopting best practices and advanced measures, every step contributes to creating a secure digital environment.
Engaging with the cyber security community, staying updated with the latest trends, and investing in continuous education and awareness can significantly enhance your cyber security posture, safeguarding your digital assets against evolving threats.
Additional Resources
Cyber Security Frameworks and Standards
Top Cyber Security Tools and Technologies
Community Forums and Cyber Security Events
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






